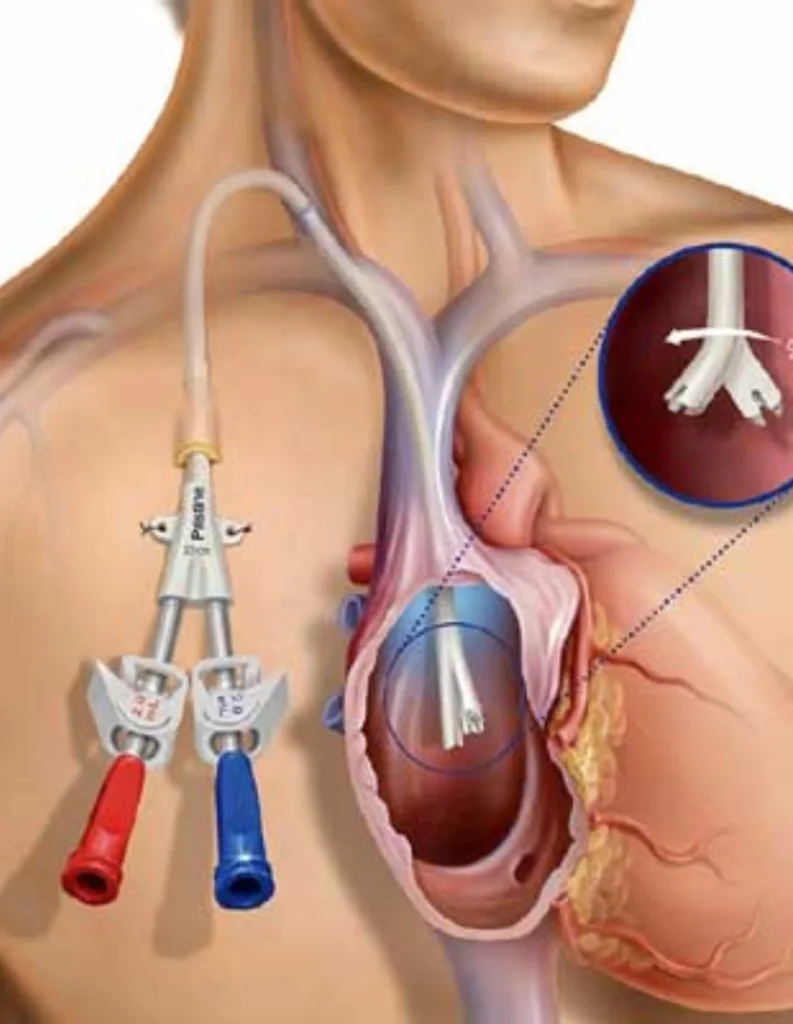
Tunneled Permanent Catheter
Caring for you, every step of the way
A Permanent Catheter, also known as a tunnelled dialysis catheter, is a tube inserted into a large vein (usually in the neck or chest). This catheter provides immediate access to dialysis, making it suitable for patients who need urgent dialysis or those who cannot have an A.V. Fistula. While it offers quick access, a Permanent Catheter has a higher risk of infection and other complications compared to an A.V. Fistula.

Symptoms
These vascular access methods are typically indicated for patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) who require regular dialysis. Indications include:
Chronic kidney failure
Regular hemodialysis requirement
Severely reduced kidney function (low GFR)
Causes for Treatment
The primary reason for establishing an A.V. Fistula or Permanent Catheter is to create reliable vascular access for patients requiring dialysis. These procedures are necessary when:
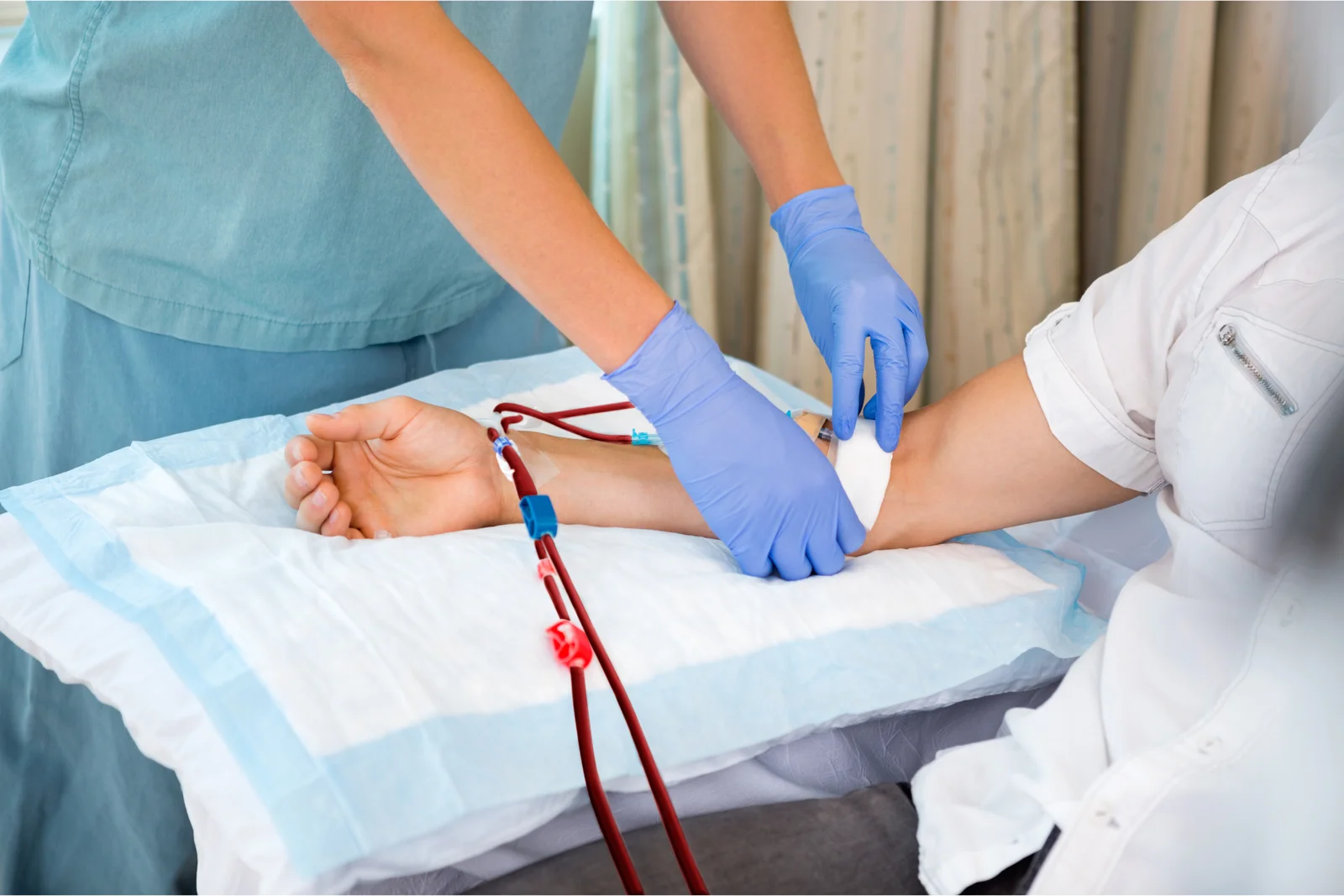

Risk Factors
There are some risks associated with both A.V. Fistulas and Permanent Catheters, including

Infection

Clotting

Permanent Catheter
Treatments
After placement, both A.V. Fistulas and Permanent Catheters require careful management to avoid complications. Patients should:

